Map and 3D World Views
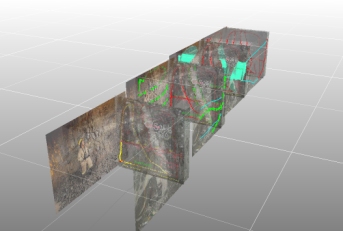
Studio Mapper's simplest georeferencing method is the "1 point method". It relies on the definition of a landmark position on the map which is translated to world coordinates. In Studio Mapper, this can be done interactively, using the 3D World view.
Once a map is georeferenced, you can continue to add features to it using the Mapping task bar and a local map window; as the same map is shown in the 3D World view, any changes are automatically reflected there also. It is generally recommended to create and edit geological elements of a map using the local map window, using the 3D World view to visualize the mapped faces in their true world positions, for example, aligned with an imported mine layout design file.
Notes:
- You can re-georeference a map in the 3D window using any of Studio Mapper's georeference methods. In this situation, your control points can be picked in either the 3D or map view.
- When a map is georeferenced, the associated image file(s) are used to generated a .jpgx file. This means, providing the .jpgx file is in the same location as the image file, you can drag/drop the images into any Studio product's 3D window, and the image wireframes will be constructed at the correct world coordinates.
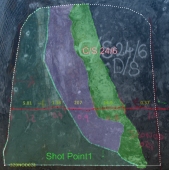
For example, the images below show two local maps in their own local coordinate system. A few features have been digitized. Each has been georeferenced using the One Point option on the Georeference ribbon. On each map, the anchor point is shown as a yellow crosshair. Map 1:
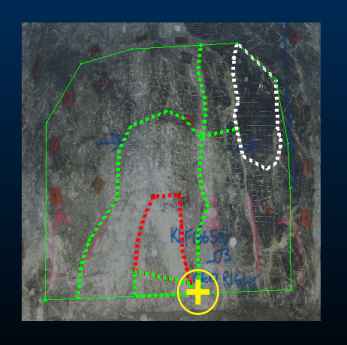
Map 2:

The second point (for each map) is picked in the 3D World view. In this case, each map's anchor point is translated to a snap point on a (red) drive design string:
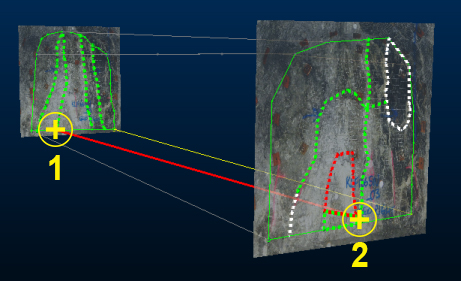
Subsequent edits to either map will now be represented in both the local map and 3D World view.
You then define the orientation of the map around this anchor point using the Rotate function (also on the Georeference ribbon), which provides an on-screen controller to adjust the orientation of the map in any of the 3 major axes, e.g.:
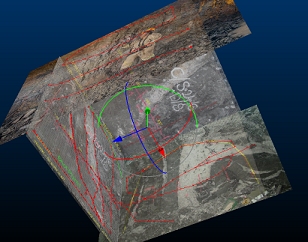
Rotation will reposition the map in 3D space, and can be performed in either a 3D World view or a Map view (both georeferenced and local maps can be rotated).
Which View?
Local (non-georeferenced) maps are only visible in a Map view as they have no context in the world view yet.
Georeferenced data opens up the 3D 'global' view to see the map in its actual world coordinates, potentially alongside other georeferenced map data and "Other files".
Which view you use for managing your georeferenced map data is up to you. You may find it easier, for example, to perform your map feature/structure digitizing in a Map view and then georeference it, or you may prefer to perform your map editing in the 3D world view.
Generally, if an uncluttered, orthogonal view of a face is needed, the Map view is recommended; swapping an active face (using the Mapping task bar) will automatically a map to view the selected face head-on. In conjunction with data clipping, this can make digitizing, sketching, commenting etc. easier than having to manually position an active face in the 3D world view.
That said, it can also be useful to view the features of neighboring drive maps to get a better sense of the overall geological feature in situ
Automated View-swapping
Studio Mapper will sometimes automatically swap between Map and World views to maintain a workflow.
For example, if you are working on a multi-face drive map that has already been georeferenced (say, new face data has recently become available) and you are currently working in a Map view, changing the face will maintain the same map view.
Similarly, you may be working on a series of face maps, some of which may not be georeferenced yet. In this situation, if a Map view is displayed and the map is changed to a different georeferenced map, the Map view is maintained (albeit for the new map, using a different map window).
In summary, window-swapping is performed as follows (in the table below "Local" means "non-georeferenced" and containing only local coordinates with the origin of the map in the bottom left of the front plane):
| Displayed | New item selected | Behaviour |
|
Local map, Map view |
New local map |
A map view of the local map is created/enabled. |
|
Local map, Map view |
New georeferenced map |
A map view of the georeferenced map is created/enabled. |
|
Local map, Map view |
New face on the map |
The map view is automatically rotated to a viewpoint that is orthogonal to the selected face. |
|
Georeferenced map, Map view |
New local map |
A map view of the local map is created/enabled. |
|
Georeferenced map, Map view |
New georeferenced map
|
A map view of the georeferenced map is created/enabled. |
|
Georeferenced map, 3D World view |
New local map |
A map view of the local map is created/enabled. |
|
Georeferenced map, 3D World view |
New georeferenced map (using Pick Map) |
The 3D World view is not adjusted but the design section will snap to the default face of the interactively pick (georeferenced) map. |
|
Georeferenced map, 3D World view |
New georeferenced map (not using Pick Map) |
The 3D World view is panned/rotated to look at the new georeferenced map |
|
Georeferenced map, 3D World view |
New face on the map |
The 3D view is maintained but the view is not adjusted. Instead, the design section (if previously aligned with the face) will automatically snap to the new face alignment. |
In this context, selection of a map is by any method (using a ribbon drop-down, the Mapping task bar, setting the current map using the Project Data controlbar and so on).
Other Ways to Change the View
All currently-available views (World or Map views) are displayed as tabs along the top of the viewing area.
Multiple local map view tabs
A "3D" world view tab is also available (providing it hasn't been hidden by some other method). You can swap between these windows using these tabs as required.
There are also other ways to trigger a view change:
- Selecting a new map in the Mapping task bar. The response will be as described in the above section.
- Double-click or tap a face in the 3D Map view to automatically orient the view orthogonally to the target face.
- Selecting a new map using any of the Draw ribbons.
- Setting a new current map using the Project Data control bar.
- Closing a 3D view window.
- Left-clicking a map view folder in the Project Data control bar.
- Left-clicking the 3D world view folder in the Project Data control bar.
- Using the Project Data control bar's context menu system to modify a non-current map.
- Left-click the Plots folder in the Project Data control bar
- Clicking into a non-current, cascaded map view where a 3D view is concurrently displayed (the 3D view will automatically update to point to the map in the active window).
-
If viewing a 3D map, change the view from a cube-style alignment of faces or a butterfly arrangement using on-screen icons.
Note: You can only swap between 3D map and butterfly map views if your configuration permits it.
There are many options when it comes to viewing data in Studio Mapper. In projects containing multiple maps and a mixture of georeferenced and non-georeferenced maps, even more options become available.
The following guidelines may help you manage your field mapping projects.
- Capture map features in a map
view before georeferencing
You can modify map data in either a Map or 3D World view, but it is often easier to digitize features, comments, sketches etc. whilst the map view is displayed. The Map view will contain only data relevant to the current map, making it easier to focus on a particular face. -
Use filled textures in your display templates
If you have a display template associated with a particular features object in your system configuration file, the legend can include textures. Closed/polygon structures on maps can then display a pattern overlay that can help differentiate structures, e.g.: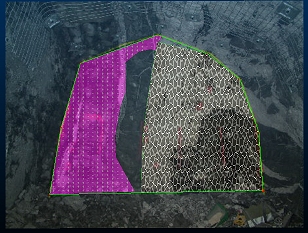
- Use clipping for multi-face maps
(drives and partial drives)
Where multiple faces exist for map, it is possible for a non-active face to partly obscure the one you're working on. Studio Mapper deals with this using smart transparency settings, but it can also be useful to clip data either side of the active plane. As the active plane is commonly aligned with the active face, clipping lets you view a face in isolation.
Clipping options are available on the 3D | View ribbon and the Navigation toolbar. - Make use of the "Pick Map"
function
The Pick Map command is available on the Map ribbon. It can be useful in a busy 3D World view as it lets you interactively pick a map to make it current and set the active section. It also automatically centers and pans the view to focus on the picked map. It's a quick way of swapping current maps in the 3D World view. - Use double-click or double-tap
to complete digitizing
You don't have to click or tap Doneto complete digitizing. Instead, you can just double-click or double-tap to end the digitizing action. This is particularly useful when sketching or digitizing map data on a tablet device. - Close a string to complete digitizing
You can complete a digitizing operation (or sketching) by closing the string, that is, positioning the final vertex at the same position as the start (commonly done using snapping), -
Consider using multiple cascaded windows
Where multiple georeferenced maps exist in the 3D World view, you can display it and associated Map views at the same time.If windows are currently maximized, click the Maximize toggle in the top right of the application:

You can arrange data windows so they are concurrently displayed, e.g.:
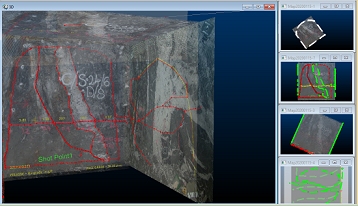
If the 3D world window is displayed, clicking into any of the available Map window thumbnails will automatically update the 3D view to show the map corresponding to the active window. This means you can make any georeferenced map current and displayed in the 3D World window just by clicking its Map window "preview". Selecting a non-georeferenced map window will not update the 3D World window.
3D Map and Butterfly Map Views
Digitize and edit map face elements using either a "3D Map" (the default view) or a "butterfly map" view, and dynamically swap between the two view types at any time.
-
3D Map views show each face as a side of a cube. Each face aligns with a particular section representing up to 5 faces (front, top/backs, left wall, right wall and floor). Changing map faces automatically orients the cube so you are viewing the target face orthogonally, for example:
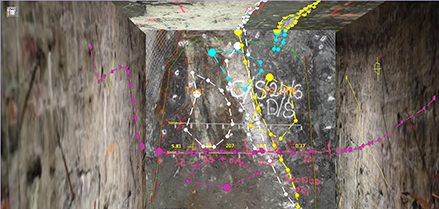
(Perspective mode is enabled in the above view. See Navigation Toolbar)
-
Butterfly map views align all faces to the same plane so they can all be viewed orthogonally at once. This can be advantageous when digitizing polygon or contact features across faces. The data shown in a butterfly map view hasn't been flattened; it simply appears that way to make it easier to create face content. For example:
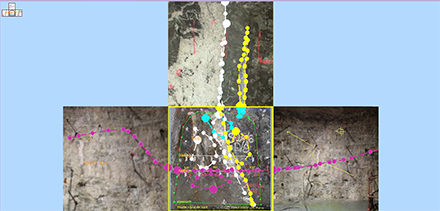
Swap between 3D map and butterfly map views instantly using the on-screen icon at the top left of the viewing area:
(1) shows the icon in 3D map mode, whilst (2) denotes the view is currently in butterfly map mode. Clicking the icon toggles between the two states.
Note: Swapping between map views doesn't affect any underlying data; only the view of the data changes. View icons do not appear in the 3D world view.
Related topics and activities
